Keeping up with rapidly evolving fintech, like open-core services, is crucial to business growth. Read on to learn more.

Open Finance aims to enable everyone to securely access and utilise financial data from multiple sources. In this article, We explore what Open Finance is, its applications and benefits, and what the future holds for the industry.
Open Finance centres around data sharing, specifically through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that enable the integration of various institutions’ data and workflows. This means that, with a user’s consent, data from one company can be automatically available to another through the use of APIs. Traditionally, data sharing is done through screen scraping, which is less secure and accurate. With APIs, consumers can share transaction data without needing to share their usernames or passwords, utilising a direct connection that delivers higher levels of security and faster speeds. Information shared can only be authorised by end-users and is transacted via an encrypted connection, with regulations provided by the Financial Data Exchange (FDX) in the US, for example. Read about Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in this whitepaper written by industry-leading tech enablers to find out more.
Open Finance unbundles financial services and products owned by banks, making them available to third parties. This unlocks huge opportunities, particularly in developing regions, where a large percentage of the population has little to no access to financial services. Companies can leverage Open Finance to find solutions that meet the needs of the unbanked, a large market ripe for growth.
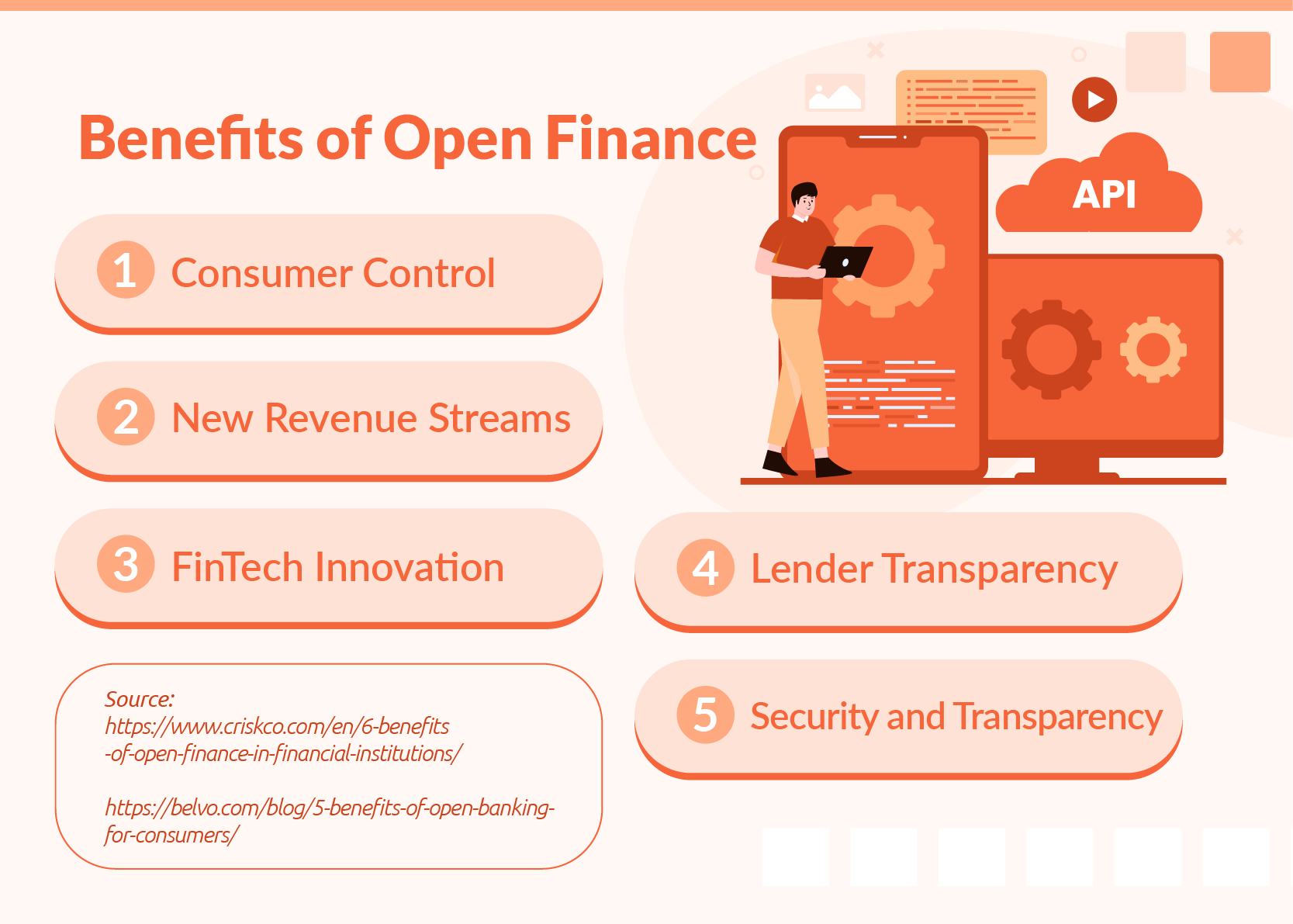
Open Finance has great benefits across the board, not just limited to the financial sector. It benefits both consumers and financial institutions by providing financial institutions with more revenue streams and consumers with more personalised products and services. Some of its benefits include:
Consumers have more choices and control over the data they share, and have access to a broader range of products and services. It provides convenience to consumers, through, for example, ‘embedded finance’, wherein all of a consumer’s financial needs are serviced within the same product.
Open Finance creates more revenue streams for financial institutions, providing a secure way for them to enable consumers to share their data with third parties. Through this, financial institutions can uncover new ways to innovate their products and create a broader range of services for their customers.
Open Finance helps facilitate the creation of new ways to use data. Fintechs can utilise this to deliver innovative and unique products to meet consumer needs. They can gain access to a broader, more accurate basis upon which to create their products, and Open Finance also creates opportunities for collaboration with government bodies or traditional financial institutions.
For lenders, the process of determining a client’s credit standing is often long and tedious, as they have to pull data from multiple sources to craft a clear picture of a client’s financials. With Open Finance, lenders can more easily pull data from multiple sources and automate the process.
One of the major challenges in developing countries is the large population of individuals who have no access to financial institutions. With Open Finance, financial institutions and fintechs can better engage with potential customers by highlighting the security and transparency, along with faster processes, that come with Open Finance solutions.
Open Finance can be used in a multitude of ways and by different industries, offering a greater variety of uses and users than Open Banking. Some of these are discussed below.
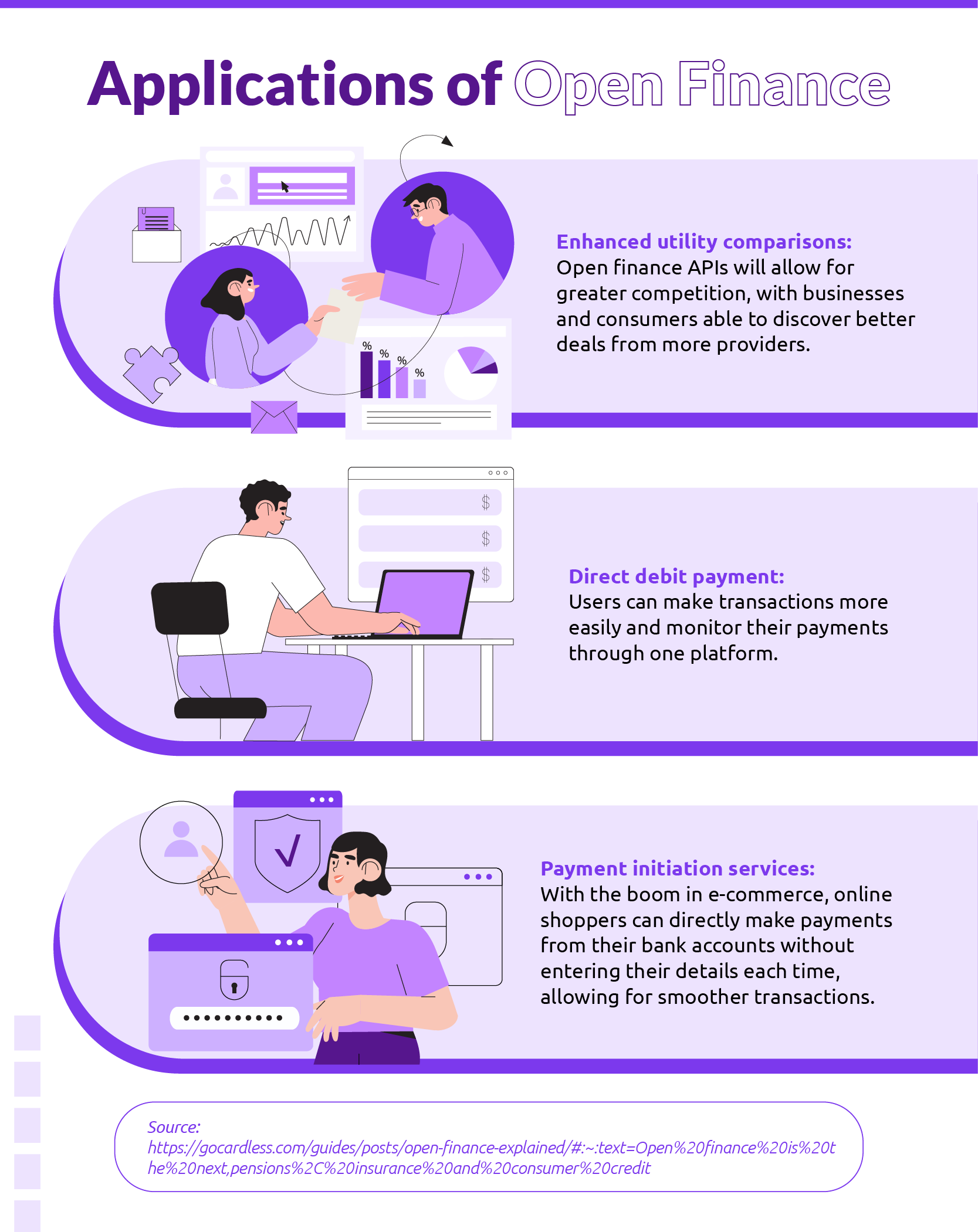
Open Finance opens up more avenues for innovation within finance, and increased collaboration among industries. Through secure data sharing, companies can innovate their product offerings further, and consumers benefit from a wider array of product options to choose from.
In Asia-Pacific, there is a 44% year-on-year growth rate of Open Banking API platforms, largely coming from Australia, Hong Kong, Indonesia, and the Philippines. This region, along with Latin America and the Middle East & Africa, has a large population and increasing regulatory commitments that make them attractive to emerging startups and fintechs looking to leverage Open Finance to create innovative products for the large population of underbanked individuals. The increased collaboration, novel product opportunities, and security established by Open Finance make it something that many companies should consider looking into to expand their reach.
Brankas is helping companies simplify their financial processes, providing customers with a wider variety of product offerings that are quick, safe to use, and accessible. In doing so, Brankas is shaping the Open Finance ecosystem in Southeast Asia – a pivotal role that can help businesses adapt to the current digital age.

Keeping up with rapidly evolving fintech, like open-core services, is crucial to business growth. Read on to learn more.

Many organizations and individuals face inadequate financial services. This inadequacy can have severe implications as it can hinder financial literacy for individuals and business growth for companies. On the other hand, financial inclusion can result in a more productive economy. But what is financial inclusion?